Has Floating Architecture’s Moment Finally Arrived?
By Rachel Keeton
Next City
October.01.2014
Resilient Cities

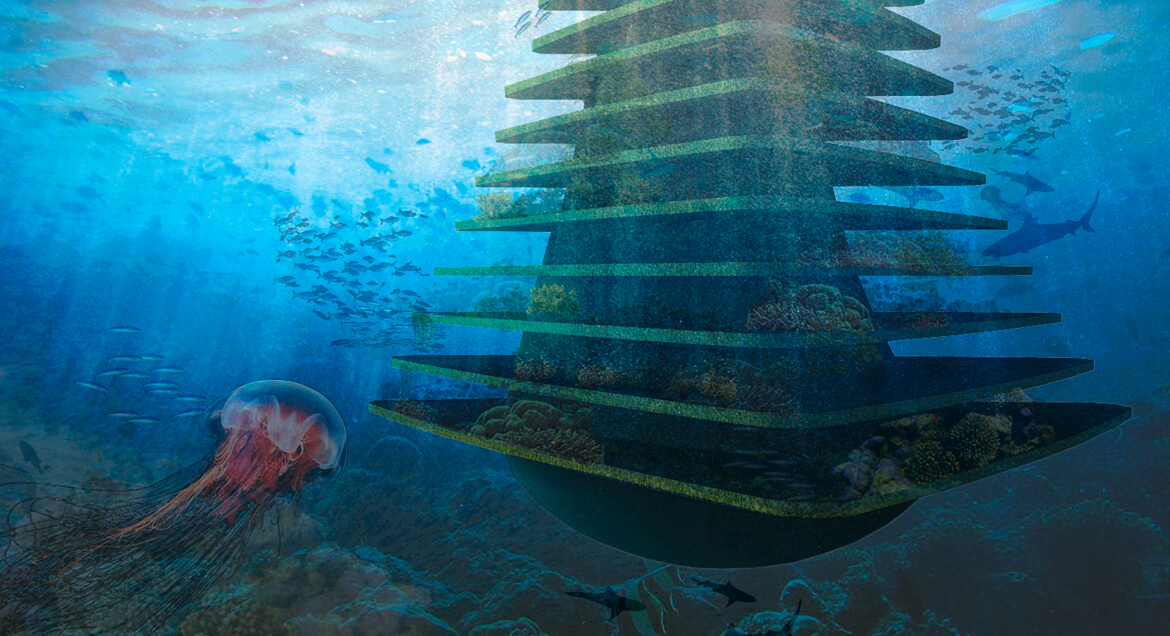
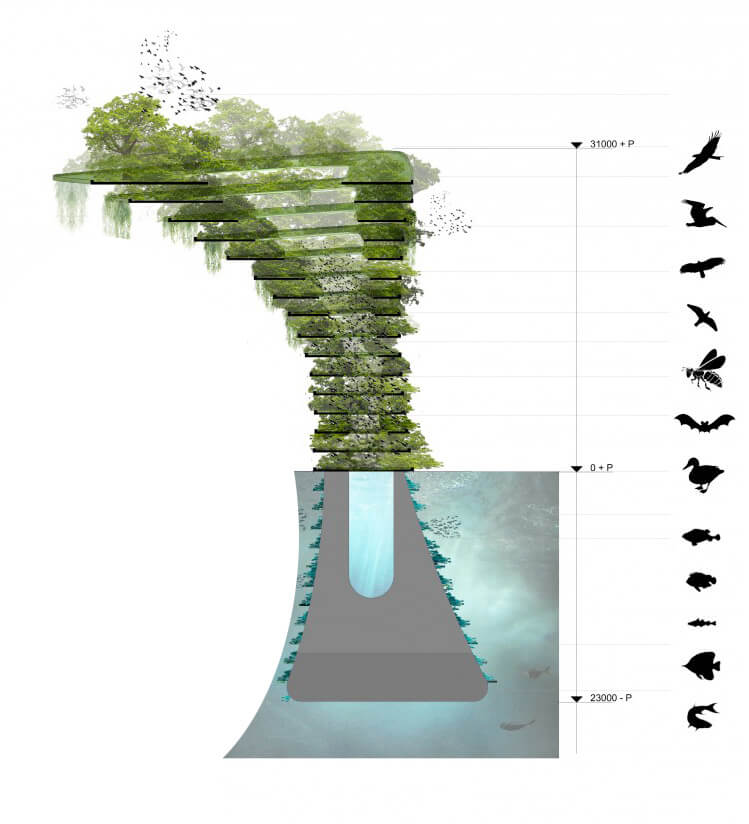
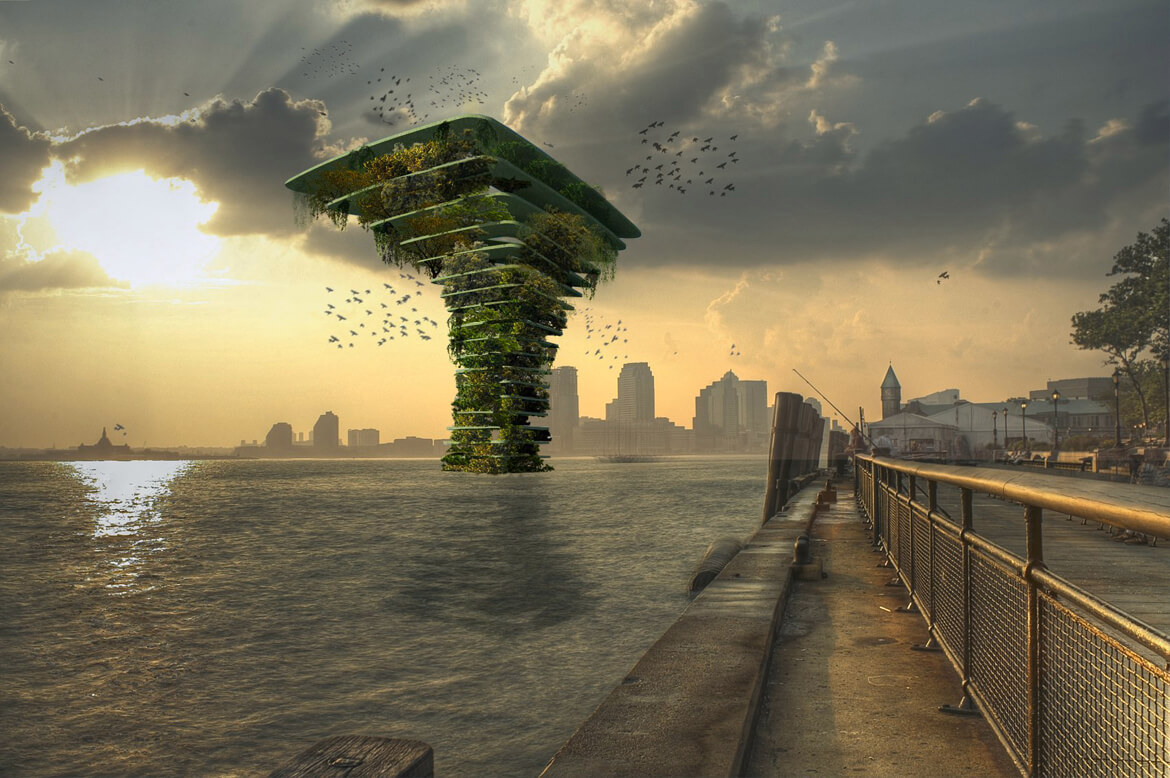
The Sea Tree, a floating natural habitat. (Photo by Waterstudio)
In a quiet, shady street in Rijswijk, the Netherlands, Koen Olthuis and the design team at Waterstudio are changing the world. From this deceptively nondescript headquarters, Waterstudio is designing the cities of the future. If Olthuis has his way, they will be safer, more flexible and more resilient than current cities. How will he do this? Olthuis is designing floating cities. As we sit down at the table, the busy office buzzing around us, my first question to Olthuis is direct: “How realistic are floating cities?” Olthuis grins and nods, he’s heard this question before.
Floating cities have captivated society’s imagination for centuries, from the development of Venice a millennium ago to Triton, designed for Tokyo Bay by Buckminster Fuller in the 1960s. But it wasn’t until the last decade or so that more fully realized, just-might-actually-happen sea-based urban endeavors have emerged, made more urgent by rising sea levels and rural-to-urban migration. In the last six months, Business Insider, Bloomberg and The Guardian have all run stories asking the same question: “Has the time come for floating cities?”
Olthuis dives right in: “It depends what you mean by ‘floating city.’ If you’re talking about a community of 100,000 in the middle of the sea, we’re probably about 50 years away from achieving that. If you want it to be completely self-supporting, it’s probably going to take another 20 years after that.” Bending over a roll of tracing paper, Olthuis quickly sketches a timeline of floating architecture. If we take it from the present moment, about midway on Olthuis’ sketch, hybrid cities are the next step in this evolution. Built on the edge of the existing city, these developments could easily connect to electrical and sanitation grids. “Technically, this stuff is easy to engineer: we’re already there,” says Olthuis. That makes them more straightforward to regulate and less risky for investors.
It’s the images of sparkling new cities lost at sea that have people raising skeptical eyebrows. “We’re working on a set of guidelines, a toolbox that will ultimately get us to the floating city you imagine. We’re working out these concepts that all give a glimpse of the future, but we have to find out what we need, how it works and what it adds to current urban development. We have to map out the steps to get us from today to the future and have to think about the entire process. And we need that, because if we don’t answer these questions, we get all these architects with beautiful renderings and fantastic ideas, but they don’t tell you the steps in-between and they don’t tell you why. And then your question is, but how realistic is it?”
Listening to Olthuis, it quickly becomes apparent that this scenario is actually incredibly realistic. With the technology and market demand in place, it’s political will and ownership issues that are holding development back. People have trouble imagining an urban future where city halls can be swapped for theaters on opening night, or entire Olympic villages can simply be towed around the world instead of rebuilt every four years. “Our cities today are too static. We make static cities for dynamic societies. We should be cities that can adapt to new demands and external influences. Water gives us three things: it adds more space (in old harbors, rivers, lakes), it’s safer (from storm conditions, rising sea levels) and it’s flexible. If you only construct the buildings you will use for 100 years statically, on land, and construct the buildings you will only use for 20 to 30 years flexibly, on water, then you’ve created a much more adaptable city that can respond to changing needs quickly and efficiently. If someone isn’t happy with their house anymore, they can ship it to someone who needs it in the Philippines.”
Governments are slowing starting to see the potential of this approach. If cities like New York or Tokyo build two to three percent of their development on the water, they can sell this to developers, tax the owners and create a more flexible city. Win-win. Governments are interested in this because it presents a new market for them. While most land is privately owned or already built up, by changing policies to make floating structures available the government expands its real estate. It’s a business model that is attractive because it solves multiple problems. Floating structures can reinvigorate former industrial areas like old harbors or riversides, they can adapt to extreme weather conditions better than traditional structures and they create a profit from space that is currently unmarketable.
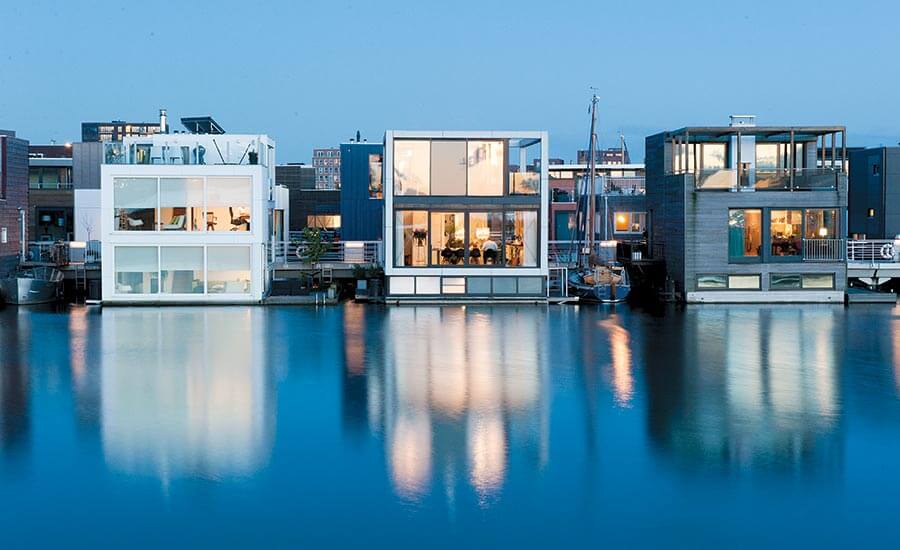
Still, the idea of bobbing around permanently makes some people understandably squeamish. If one floating house goes up and down on waves, it may tilt: one half sits on the crest of a wave and the other end is stuck in the trough. This doesn’t happen when you start to build big enough to have a project that is always supported by multiple waves. On the water, the bigger the project, the more stable is it. In fact, floating cities are actually something that works better all around on a larger scale. If Olthuis is designing a watervilla for a single family, he has to calculate all kinds of factors to design a single, site-specific home. This ends up costing a lot more than a traditional house. If he’s designing a community of 10,000 water villas, the price is the same as a comparable urban development.
Moving functional amenities like prisons, stadiums and airports onto the water is already becoming more common as cities try to create more elbowroom for residents. Alvaro Siza’s recently completed chemical plant in Huai’An City, China, was built on the water, and BREAD Studio recently designed a floating cemetery to be rafted off the coast of Hong Kong – a city long on elderly citizens but short on space. Today there’s a floating skate park on Lake Tahoe and floating freshwater pools in the River Thames. There’s even a floating cinema in London by UP Projects, echoing Aldo Rossi’s iconic Il Teatro del Mundo from 1979.
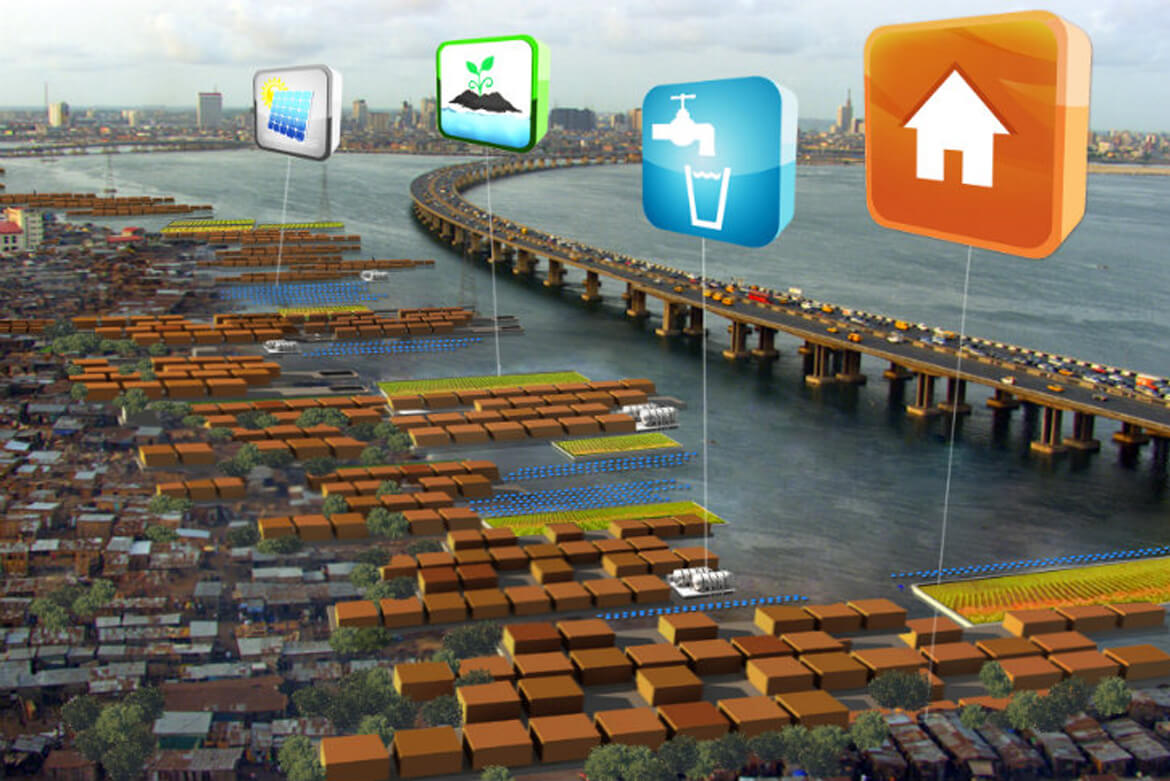
Less whimsical but more crucial are floating developments for informal settlements located on waterfronts or in delta regions that are most vulnerable to rising sea levels. Kunlé Adeyemi’s floating school in Makoko, a picturesque shantytown in Lagos, Nigeria, will provide classroom space for 100 students. The problem with one-off projects like NLE’s floating school, according to Olthuis, is that the Lagos government has been against it from the beginning (it’s been declared illegal), and it’s not even being used because of this controversy. “If you want to really make a difference, it can’t be just one thing. It has to be a system with a sound business model,” says Olthuis.
“I think the current generation of architects really wants to help, they want to make a difference. If you tell the story of one billion people living in slums in places like Thailand, India, Bangladesh — where water is threatening those people and no one is helping them because anything that gets built can be wiped out by the next tsunami — we think, well we have to help those people. The City Apps project — retrofitted shipping containers floating on trash — is a system where we bring in floating schools, sanitation, electricity, water treatment facilities, bakeries, internet cafes, or whatever is most needed. We can connect these floating functions to the slums or disaster sites and they will slowly help upgrade these areas.
We’re investing in this ourselves, by funding the first prototype that will be deployed to Manila. We’ve started a foundation, working with Cordaid, where we lease the City Apps directly. It costs us about €50,000 to design and build a City App in a recycled shipping container, then it gets deployed to wherever it’s needed and there they construct a floating platform out of old plastic bottles and other rubbish. Ultimately, it should be a business model that provides an entrepreneurial opportunity for residents of these areas. It’s cheap — they just pay a small monthly fee — it’s safe, since it goes up and down with the water, and it provides a solution to real problems. If you don’t need it anymore, you just send it back to us and we lease it out to someone else. Next year we’ll have ten, the year after, a hundred, and it will grow to a few thousand containers around the world. Of course, it’s just a small help to these millions of people, but we hope it will act as a model and show that we can shift from giving aid to providing an opportunity for employment.”
On the other end of the inclusiveness spectrum, there are politically motivated projects like the Seasteading Institute’s Floating City. Promoted with viral videos and backed by private donors and crowd funding, these mobile communities are envisioned as new experiments in governance, giving each community total political autonomy over itself. After attending the third Seasteading Institute conference in 2012, Josh Harkinson of Mother Jones summarized the Institute as “a hacker’s approach to government with a Waterworld-esque conception of Manifest Destiny. More than a mere repository for political dreamers, it brings together engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs of the sort one often finds in the Bay Area: techtopians who might be brilliant or delusional — or both.”
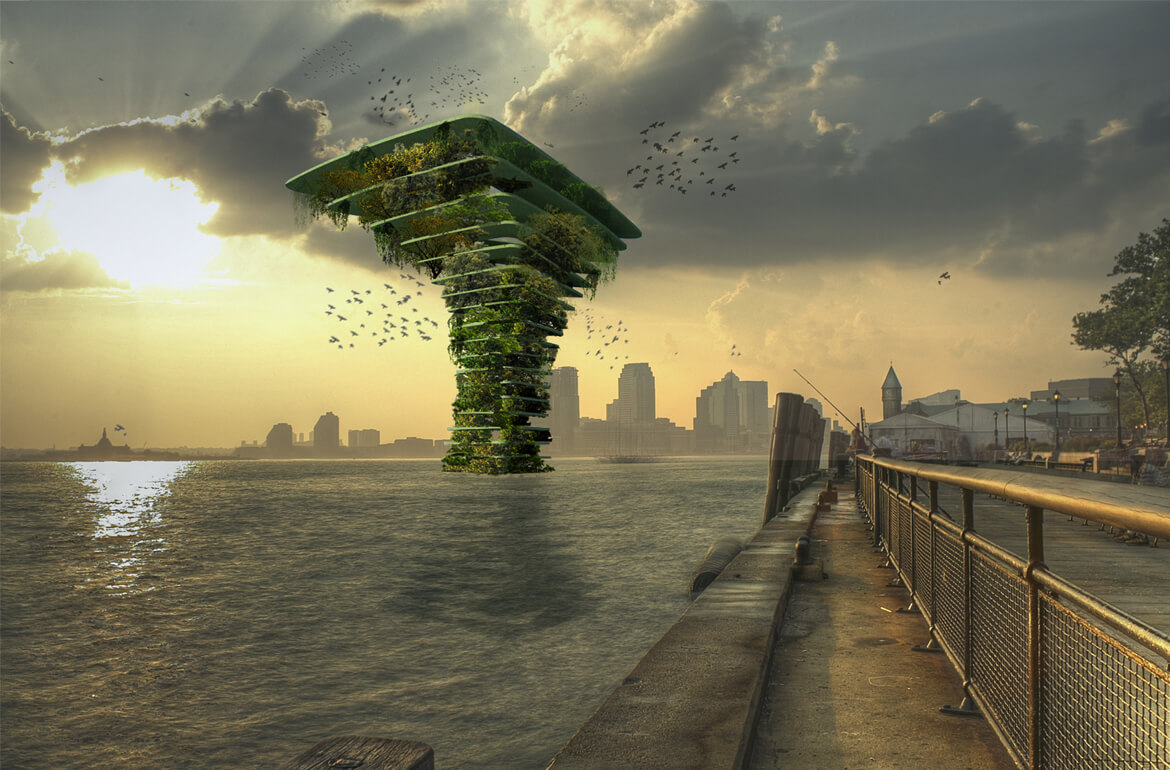
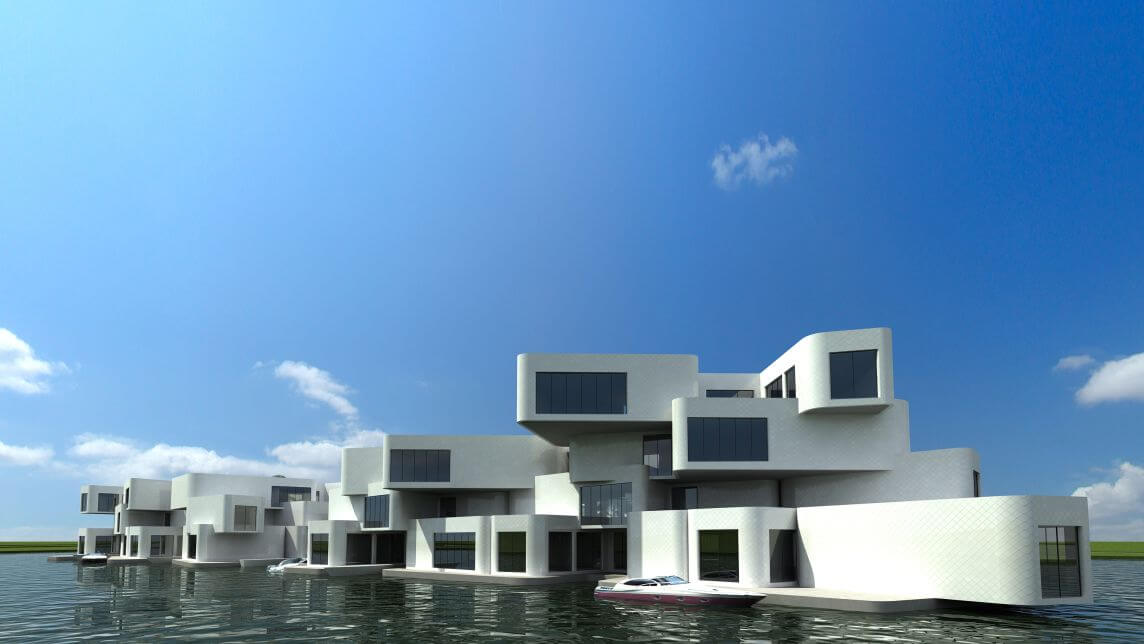
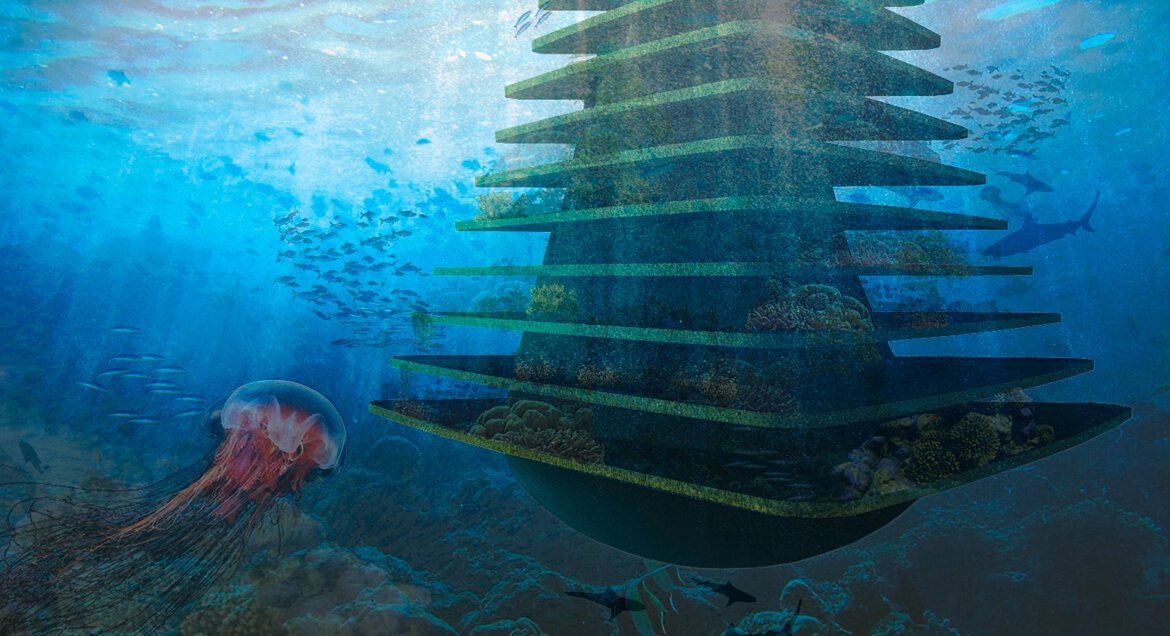
Olthuis accepts that different floating communities may have different goals. “I think we’ve only seen about 10 percent of the ideas that are actually possible in terms of floating architecture. In the next century, we’ll have thousands and thousands of new architects who can think about these possibilities.” Waterstudio calls their floating designs “scarless,” meaning they can be repositioned without leaving any trace of their presence. But the next step is to build designs like the Sea Tree, a floating natural habitat that would give small fish a sanctuary, increase the oxygenation of water, and potentially collect trash as it drifted about.
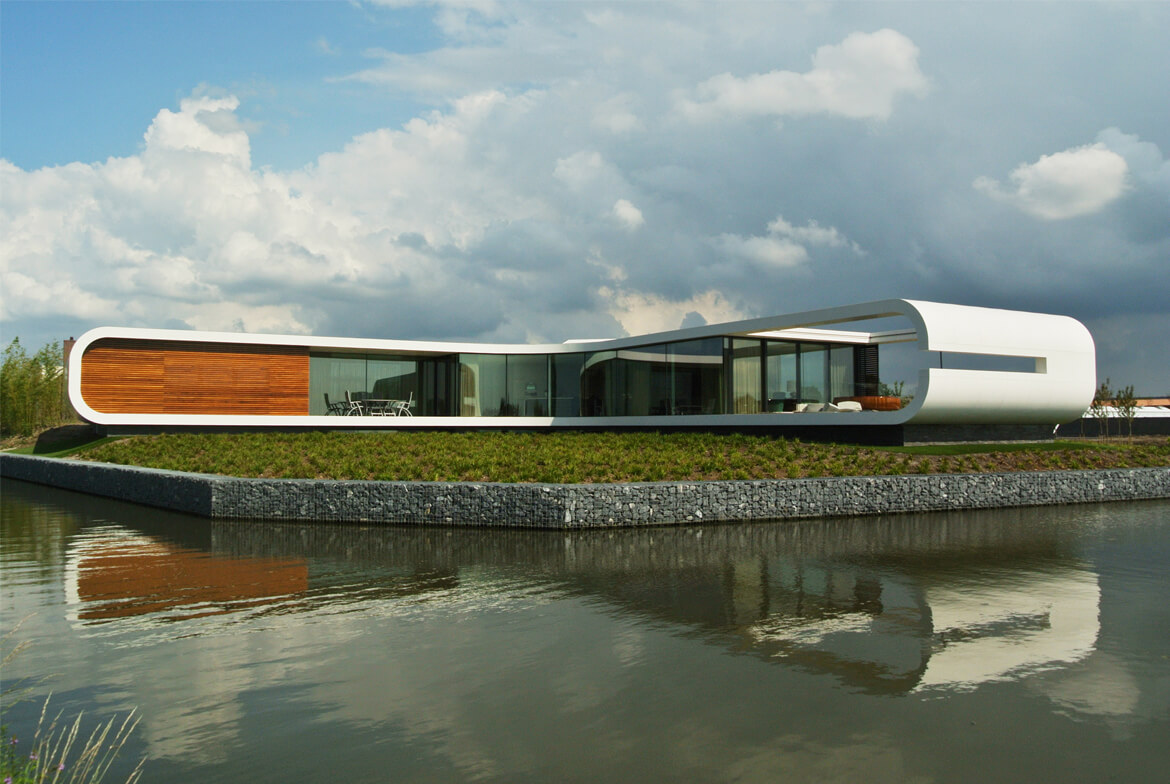
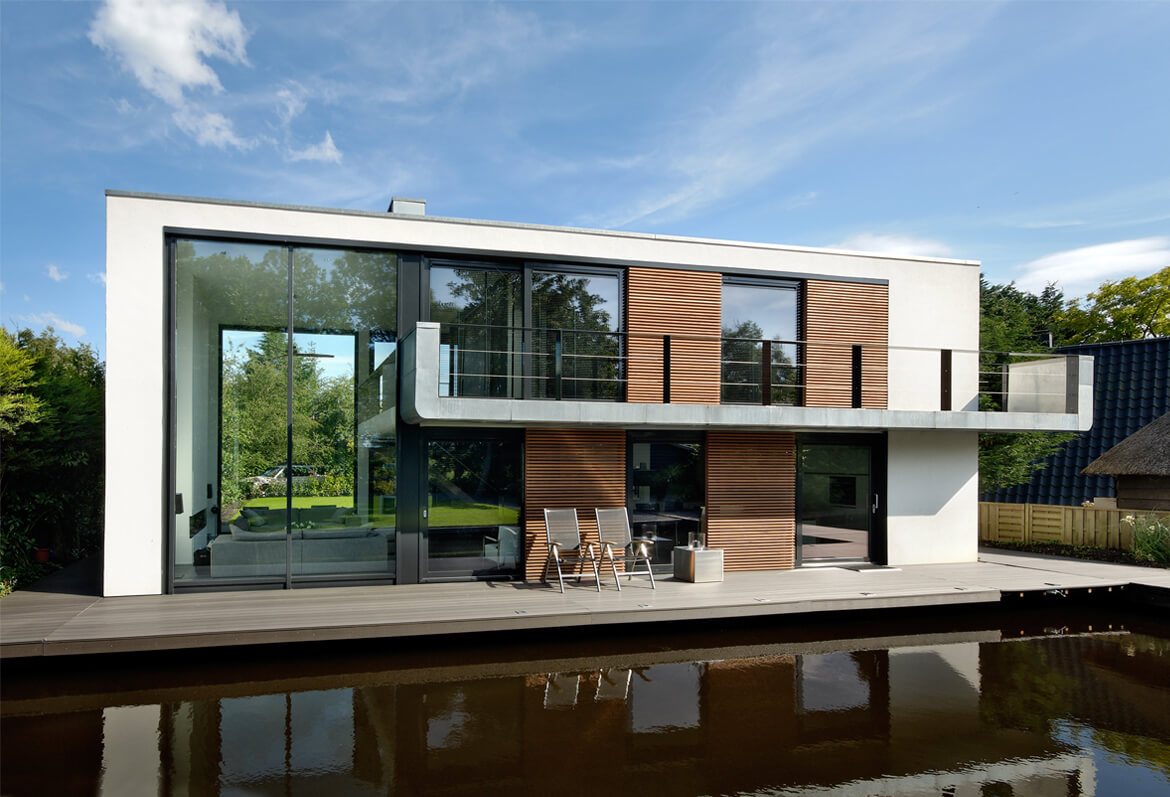
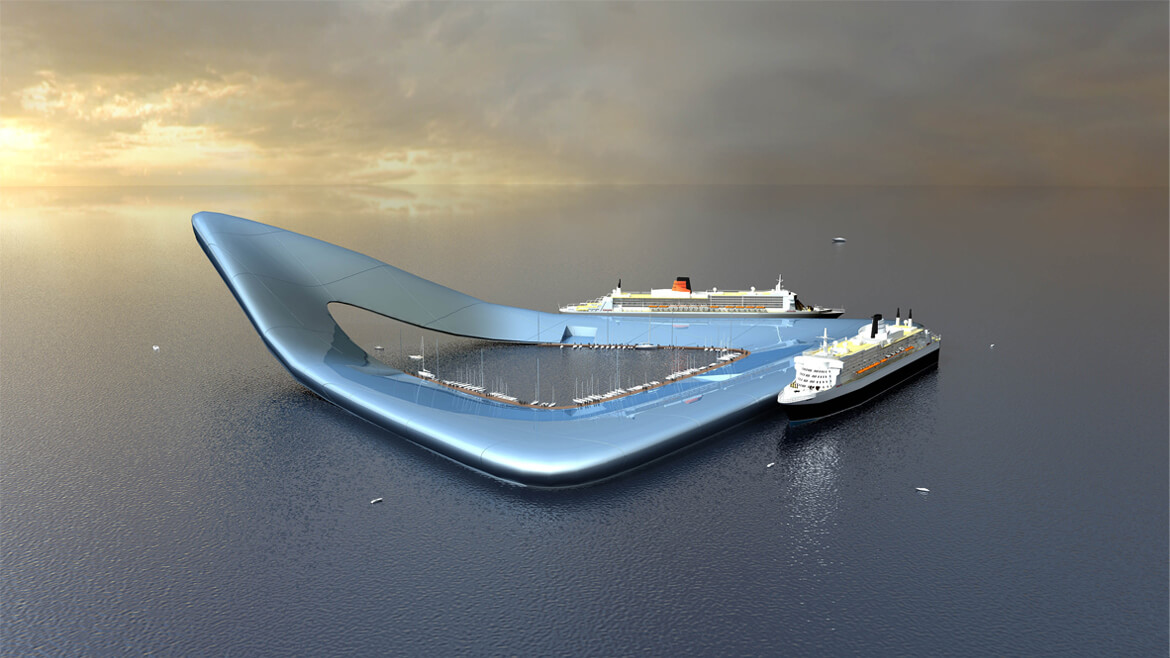
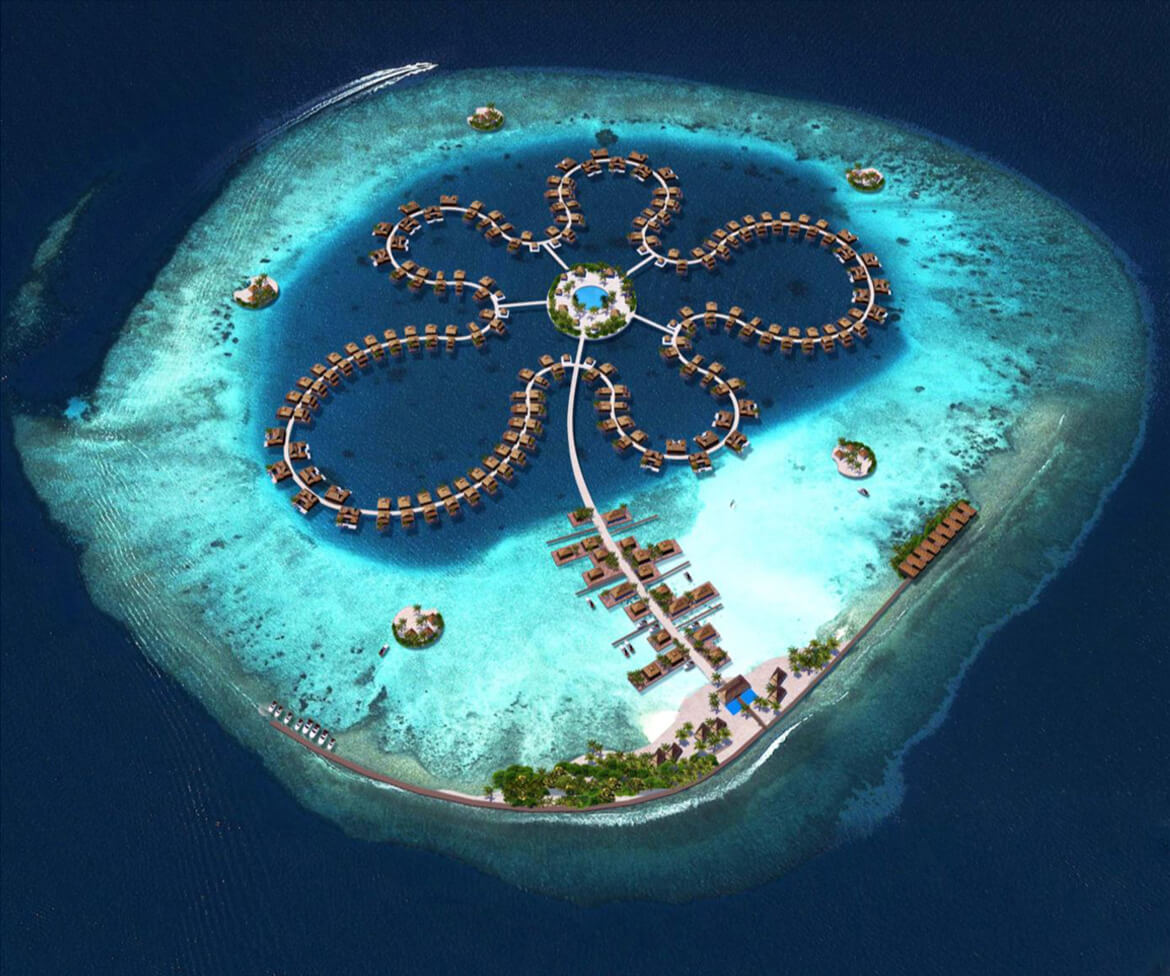
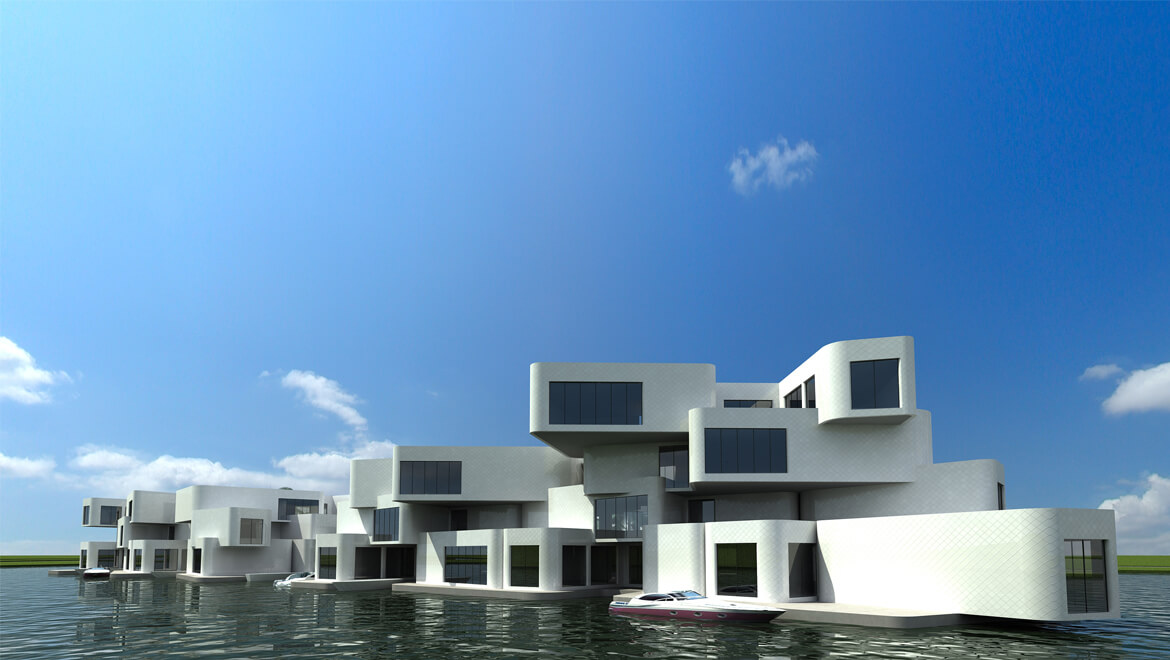
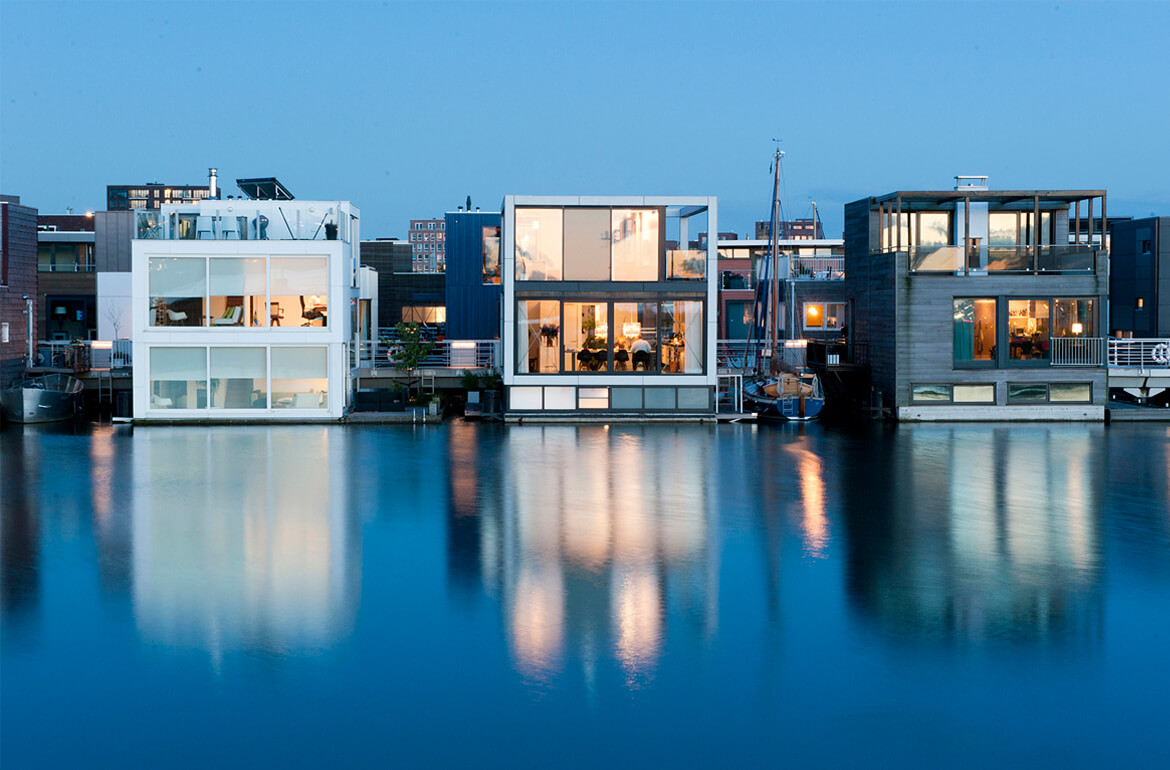
Olthuis is adamant that we have to embrace the water rather than run from it — we don’t have any other options. “Today, the momentum is there because we see the effects of climate change and we can’t be sure about our safety. We see millions of people moving to the cities and we don’t know where they will live. These issues are finally making people think twice about floating architecture. If we can convince them that it’s also financially profitable and help governments change building regulations, we’ll have a future where it’s normal to see cities that are 95 percent built on land and five percent built on water — just enough to give them the flexibility they need for an uncertain future.” It’s a revolutionary way of thinking about the city: puzzle pieces that can be reconfigured according to changing needs and desires. Olthuis’ concern with marketability and political interest makes his story much more convincing than the glossy renderings popping up on design websites. “Many architects are using technical solutions to approach this problem and just showing us the images without any information. I think a floating city is only something that works when it makes sense economically, socially, spatially — and should also look nice. It should be a normal development that is open to everyone, rather than an alien form for an elite few.” His belief in the advantages of these projects is clear, and the built examples in the Maldives, China and the Netherlands are proof of their viability. Just as it was for Buckminster Fuller 50 years ago, the floating city remains an exciting and mysterious model of urban development. Only now, it’s closer than ever. And Koen Olthuis can tell you exactly how to build it.


 By Tanja Lina
By Tanja Lina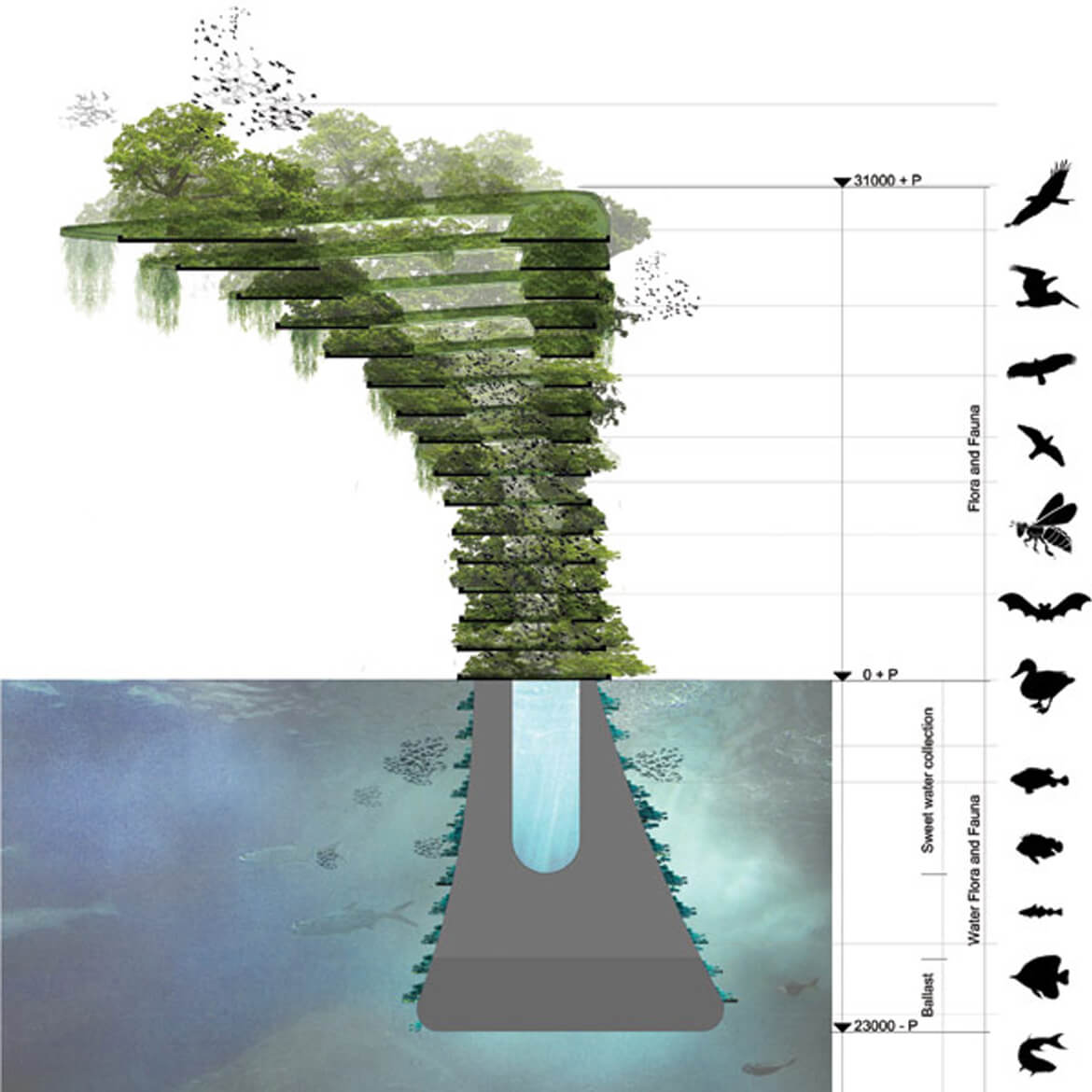















 By Haus mit Zukunft
By Haus mit Zukunft